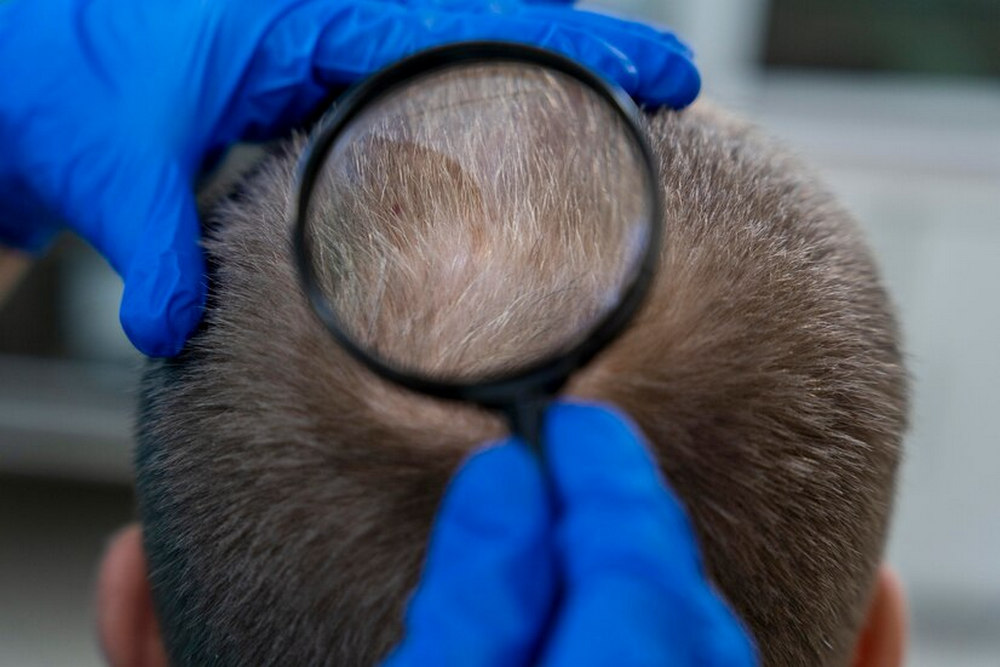
Nothing gets our attention more than seeing hair in the shower drain or in a comb. When that happens, we start looking in the mirror to check out our thinning hair and wonder: Why am I losing so much hair? Are my genes causing me to lose it?
What is the baldness gene, what are its causes?
Hair loss is a multifactorial phenomenon, influenced by hormonal, environmental and genetic factors. The AR gene is responsible for encoding a protein called the androgen receptor, which influences male sexual development during fetal development, puberty and adolescence.
There are more than 600 mutations in the AR gene that cause androgen insensitivity. Those that are related to hair loss are those that affect the coding of the androgen receptor protein as they trigger reactions that shorten the hair growth cycle.
Androgen insensitivity is an inherited syndrome with an X-linked pattern. In males (XY chromosomes), a mutation in the gene is sufficient to increase the risk of hair loss, whereas in females (XX chromosomes) there would have to be a mutation in both chromosomes.
This explains why men are affected by baldness more frequently than women, and also why male pattern baldness is associated with maternal genetics.
Let’s Explore the Myths and Facts
Many stories about baldness have been passed down from generation to generation, most of which are not based on fact. For example, it is not true that wearing hats, excessive hair washing and having too much testosterone cause baldness. The reality is that in many cases hair loss is temporary and can be due to many different things, such as:
- Autoimmune system or thyroid diseases.
- High levels of stress
- Nutritional deficiency
- Hormonal changes after childbirth
- The normal life cycle of hair follicles, which enter a “resting” (telogen) stage.
In most cases of alopecia, the cause is genetics. And if you have the baldness gene, it is a completely natural process, which cannot be stopped.
It’s Called “Androgenic Alopecia”
Better known as male or female pattern baldness, androgenic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss. It’s characterized by a slowly receding hairline and thinning at the crown, and, yes, it is passed down through heredity. But contrary to the popular myth, it can be inherited from both the male and female parents, not just from the mother’s side.
The baldness pattern usually begins early in adulthood, when a hormone called dihydrotestosterone, (DHT) begins to affect hair follicles. DHT is a by-product of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, which is responsible for the development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty. And although DHT performs a lot of essential functions—like helping us build muscle mass—it’s unfortunately where the problem lies.
If you’re genetically predisposed for baldness, DHT acts on the life cycle of your follicles, causing hair to gradually shrink and to grow back more slowly after it falls out. Eventually, the follicles stop producing altogether, resulting in permanent bald spots. This process speeds up as men get older, and even women aren’t immune to its effects as they age.
How is it diagnosed?
Androgenic alopecia is diagnosed by evaluating different factors:
- Detailed clinical history. The specialist asks the patient about the age of onset of hair loss, family history, diet, stress, systemic diseases and previous treatments.
- Physical examination. The pattern of hair loss, hair density, scalp condition and the presence of dermatological conditions are evaluated.
- Blood tests. In some cases a blood test may be ordered to identify mutations associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS). That is, mutations in the AR gene.
- Capillary biopsy. Although rare, a biopsy is performed to evaluate the structure and health of the hair follicles.
How common is this type of baldness?
Androgenic alopecia is the main cause of baldness. It is estimated that more than 60% of men and about 50% of women during their lifetime.
How to Lighten the Impact of Baldness?
Unfortunately, there’s no reversing genetically-inherited baldness, but there are some things you can do.
- Consider restorative treatments. If your hair loss is becoming serious, you have options, such as mesotherapy, which is the injection of nutrients directly into the scalp. Another alternative is to get hair grafts (transplants) which take hair from thriving parts of your scalp and “plant” them in thinning areas, where they’ll grow. Although it’s technically a minor surgery, many find it an attractive option because it offers long-term results.
- Rule out any health problems that might cause you to lose hair. Sudden, excessive hair loss may an indicator of a bigger problem, such as alopecia areata, a condition that causes your own immune system to attack your hair follicles. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) and certain diseases affecting the reproductive system may also be linked to hair loss.
- Make sure you maintain proper nutrition. Like any other part of your body, your hair needs the right nutrients to grow. A diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins should provide you with all the essential vitamins your hair requires, as well as certain minerals like zinc. If you can’t get all of these in your foods, discuss taking supplements with a healthcare provider.
- Reduce your stress level. Stress is the body’s enemy on so many fronts, not least of which is your hair. Excessive stress causes the release of large quantities of hormones that can damage hair follicles and can even bring about premature greying. Chronic stress also results in high levels of cortisol, a hormone that’s associated with weight gain.
- Shampoo with good quality hair care products. For the best results, select shampoos with all natural ingredients that nourish the scalp and avoid those with perfumes or other additives that can be damaging to your hair. Shampoos fortified with nutrients such as biotin (Vitamin H) or pantothenic acid (Vitamin B5) will help keep your hair strong.
- If you have already done all the previous options, or you are looking for something more effective and lasting against alopecia, opting for a hair graft is a great option.
It will be with your own hair, removing a little of the back part to implant it in the areas where you want, this through the FUE/DHI technique that will look quite natural.
Let Us Help
Don’t go it alone—The Hair Fix Restoration Clinic is eager to discuss your treatment options with you, regardless of where you are in the hair loss process. When you come to Hair Fix, you’ll be met by experienced, top-rate doctors and nurses in our state-of-the-art facility in Tijuana. We offer the best care anywhere around, and at a lower expense than you’d find in the United States. Contact us today for a free consultation and get started on your journey to healthy hair. Ask us about stem cell therapy for hair loss in Tijuana, hair transplantation in Mexico.